Dihydrotestosterone
From DrugPedia: A Wikipedia for Drug discovery
|
|
| Dihydrotestosterone
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H30O2 |
| Mol. mass | 298.33 |
| SMILES | & |
| Synonyms | Androstanolone |
| Physical data | |
| Melt. point | 181(EXP) °C |
| Solubility in water | 5.25E+05(EXP) mg/mL |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral 0-2% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
Schedule III (US), Schedule IV (CA) |
| Routes | Intramuscular, transdermal |
Contents |
[edit] Description
A potent androgenic metabolite of TESTOSTERONE. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is generated by a 5-alpha reduction of testosterone. Unlike testosterone, DHT cannot be aromatized to ESTRADIOL therefore DHT is considered a pure androgenic steroid.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (Full name: 5α-Dihydrotestosterone, abbreviating to 5α-DHT; INN: androstanolone is a biologically active metabolite of the hormone testosterone, formed primarily in the prostate gland, testes, hair follicles, and adrenal glands by the enzyme 5α-reductase by means of reducing the 4,5 double-bond. Dihydrotestosterone belongs to the class of compounds called androgens, also commonly called androgenic hormones or testoids. Androgens are part of the biology of gender by stimulating and controlling the development and maintenance of masculine characteristics. DHT is 3 times more potent than testosterone; testosterone is 5-10 times more potent than adrenal androgens.<ref>[1]</ref>
While DHT is best known for its roles in causing male pattern hair loss and prostate problems, it is crucial to virilization and is necessary to mitigate estrogen's effects in men.
[edit] General Properties
*Molecular Weight
290.44
*Molecular Formula
C19H30O2
*IUPAC NAME
(5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
*Canonical Smiles
CC12CCC(=O)CC1CCC3C2CCC4(C3CCC4O)C
*Isomeric Smiles
C[C@]12CCC(=O)C[C@@H]1CC[C@@H]3[C@@H]2CC[C@]4([C@H]3CC[C@@H]4O)C
[edit] PhysioChemical Properties
*Melting Point
181(EXP)
*LogP
3.55(EXP)
*Water Solubility
5.25E+05(EXP) at 25C
[edit] Significance
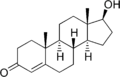
DHT is produced by males in vivo and is responsible for the formation of male sex-specific characteristics. DHT is an important contributor to other characteristics generally attributed to males, including facial and body hair growth, and deepening of the voice. DHT may also play a crucial role in both sex drive and the growth of muscle tissue.<ref>Max Muscle Sports & Fitness</ref>Template:Verify credibility Unlike other androgens such as testosterone, DHT cannot be converted by the enzyme aromatase to estradiol<ref>Dihydrotestosterone: a rationale for its use as a non-aromatizable androgen replacement therapeutic agent</ref>. It, therefore, is frequently used in research settings to distinguish between effects of testosterone caused by binding to the androgen receptor, and those caused by testosterone's conversion to estradiol and subsequent binding to estrogen receptors.
[edit] Pathology
DHT is the primary contributing factor in male-pattern baldness. This is not the case for women; female-pattern baldness is characterized by increased rates of production of testosterone, but not of DHT.<ref>Production rates of testosterone and of dihydrotestosterone in female pattern hair loss</ref> Women with increased levels of DHT may develop certain androgynous male secondary sex characteristics, including a deepened voice and facial hair. DHT may play a role in the development or exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH, and prostate cancer, by enlarging the prostate gland.<ref>http://tuberose.com/Prostate.html</ref> Unfortunately the role of DHT on the prostate is not completely understood. There are some theories that the combination of DHT with other changes in other hormones such as increasing estrogen may be a factor. <ref>http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/full/23/30/7546</ref> There are theories that indicate DHT injections can actually be used to treat benign prostate hypertrophy. The clinical application of this theory is discussed in US patent 5,648,350 Dihydrotestosterone for use in androgenotherapy. As such more research is required and there are studies underway to help understand the role of DHT on the prostate. <ref>http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00490022</ref>
DHT is also known to participate in the development in some cases of acne.Template:Fact
[edit] Treatment
The drugs belonging to the group known as 5α-reductase inhibitors are used for treatment of problems stemming from DHT. This group includes finasteride (sold under the names Proscar for BPH and Propecia for androgenic alopecia as well as in generic formulation) and dutasteride (sold under the name Avodart). Dutasteride is three times more potent than finasteride inhibiting the type II enzyme and 100 times more potent than finasteride inhibiting the type I form of the DHT producing enzyme. Dutasteride is not approved by the FDA for the treatment of Male Pattern Hair Loss and is approved at a dose of 0.5 mg a day for the treatment of prostate enlargement. While both the type I and type II enzymes are found in the hair follicle, there is a recent study which shows that type I is present in the human brain. The function of this enzyme in the brain is still unclear.<ref>Update on Dutasteride | IAHRS Hair Transplant & Hair Loss Info Center</ref>
Currently, DHT supplementation is not used as a treatment for DHT/androgen deficiency.
[edit] External Links
- [2]Pubchem
- [3]]1D2S,[[4]]1F5F,[[5]]1KDK,[[6]]1KDM,[[7]]1T73,[[8]]1T74,[[9]]1T76,[[10]]1T79,[[11]]1T7F,[[12]]1T7M,[[13]]1T7R,[[14]]1T7T,[[15]]1T5Z,[[16]]1T63,[[17]]1T65,[[18]]1XJ7,[[19]]2AMA,[[20]]2PIO,[[21]]2PIP,[[22]]2PIQ,[[23]]2PIR,[[24]]2PIT,[[25]]2PIU,[[26]]2PIV,[[27]]2PIW,[[28]]2PIX,[[29]]2PKL,[[30]]2QPY,[[31]]2Z4J,
- [32]]KEGG Compound
- [33]]KEGG Drug
- [34]Human Metabolome DataBase
- [35]Drugbank

